China Tyre Sourcing Guide: An In-depth Look into Chinese Tire Manufacturing
China has solidified its position as a global powerhouse in the manufacturing industry, and the tire sector is no exception. With advanced production capabilities, competitive pricing, and a vast array of product offerings, Chinese tire manufacturers have become a compelling choice for global buyers. This comprehensive guide aims to equip importers with essential knowledge, from understanding diverse product types and key specifications to identifying leading manufacturers, navigating certification requirements, and making informed purchasing decisions.

I. Introduction to Tyre Types
The Chinese tire industry produces a wide spectrum of tires, catering to various vehicle types and applications. Understanding these categories and their specific characteristics is crucial for effective sourcing.
1.1 Passenger Car Tires (PCR)
Passenger car tires are designed for sedans, SUVs, and light trucks. They prioritize comfort, fuel efficiency, low noise, and safety for everyday driving. Key performance indicators include wet and dry grip, braking distance, and tread life. Chinese manufacturers offer a full range, from budget-friendly options to high-performance and ultra-high-performance (UHP) tires, as well as specialized tires for all-season, winter, and summer conditions.

1.2 Commercial Vehicle Tires (TBR - Truck and Bus Radial)
TBR tires are built for heavy-duty applications, including trucks, buses, and commercial vans. Durability, load-carrying capacity, and fuel efficiency are paramount for these tires. They are designed to withstand long hauls, varied road conditions, and continuous heavy loads. Common types include steer tires (optimized for steering control), drive tires (for traction), and trailer tires (for free-rolling applications). Chinese TBR tires are renowned for their robust construction and cost-effectiveness.

1.3 Agricultural Tires (AGR)
Agricultural tires are specifically engineered for farm machinery such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation equipment. Their primary function is to provide superior traction on soft, muddy, or uneven terrain while minimizing soil compaction. AGR tires feature deep, aggressive tread patterns (e.g., R-1, R-1W, R-2 for varying mud conditions; R-3 for sandy soils; I-1, I-3 for implements) and robust sidewalls to handle demanding agricultural environments. Flotation, stability, and resistance to punctures are critical.

1.4 Off-the-Road (OTR) Tires
OTR tires are massive, durable tires used on heavy equipment in industries like construction, mining, port operations, and earthmoving. Vehicles such as loaders, bulldozers, dump trucks, and graders rely on OTR tires. These tires are characterized by their immense size, extremely deep treads, and reinforced construction to withstand extreme loads, harsh surfaces, and abrasive conditions. They come in various patterns optimized for rock, traction, or floatation.

1.5 Industrial Tires
Industrial tires are designed for material handling equipment like forklifts, industrial tractors, and other specialized machinery operating in factories, warehouses, and industrial sites. They prioritize stability, load-bearing capacity, and puncture resistance on paved or concrete surfaces. Both solid (puncture-proof) and pneumatic (air-filled) options are available, depending on the application.
II. Main Specifications and Parameters
When procuring tires, understanding the universal sizing and performance parameters is crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
2.1 Tire Size Code
A typical tire size, such as "205/55R16 91V," decodes as follows:


205: Section Width (in millimeters) – The width of the tire from sidewall to sidewall.
55: Aspect Ratio – The height of the sidewall as a percentage of the section width. In this case, the sidewall height is 55% of 205mm.
R: Construction Type – "R" stands for Radial construction, which is the most common type due to its flexibility, fuel efficiency, and long tread life. "B" would indicate Bias-ply construction, typically found in older or specialized applications.
16: Rim Diameter (in inches) – The diameter of the wheel rim the tire is designed to fit.
91: Load Index – A numerical code indicating the maximum load capacity the tire can carry. A load index of 91, for example, corresponds to 615 kg (1356 lbs) per tire.
V: Speed Rating – An alphabetical code indicating the maximum speed the tire is designed to handle safely. "V" signifies a maximum speed of 240 km/h (149 mph).
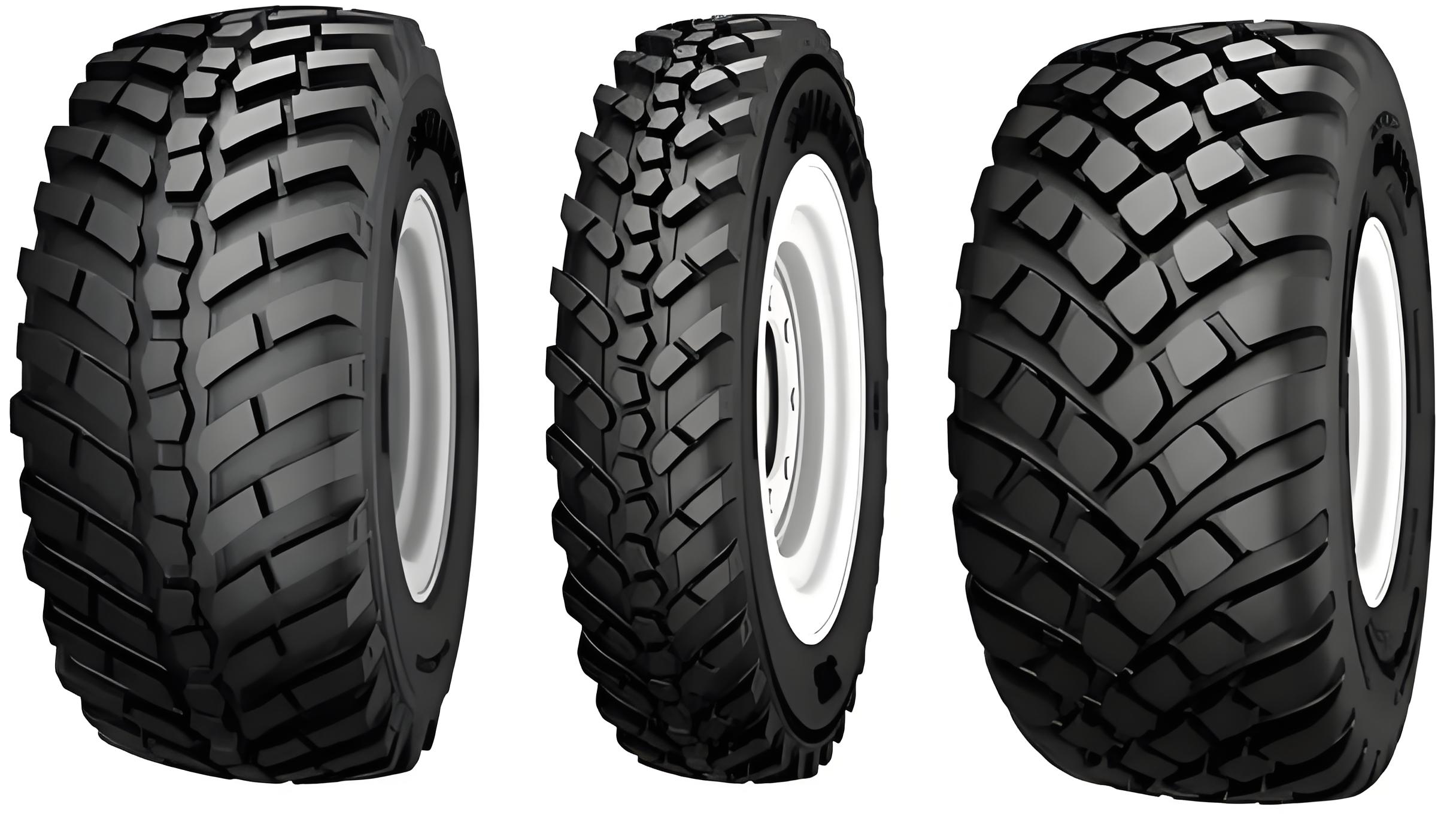
2.2 Tread Pattern
Tread patterns are designed for specific purposes:
Rib (Straight Groove): Excellent steering stability, low rolling resistance, good drainage, and low noise, often found on passenger car and steer axle tires.
Lug (Transverse Groove): Superior traction, braking, and driving force, with excellent wear resistance, common on drive axle tires for commercial vehicles and OTR tires.
Rib-Lug (Mixed): Combines the advantages of both, offering good steering and traction.
Asymmetric: Different patterns on the inner and outer sides for optimized wet and dry performance.
Directional: Designed to rotate in one direction for enhanced wet traction and hydroplaning resistance.
2.3 Ply Rating/Load Range
This indicates the tire's strength and maximum load capacity, particularly relevant for commercial and OTR tires. It's often represented by a "Ply Rating" (e.g., 14PR, 16PR) or a "Load Range" letter (e.g., Load Range E, Load Range F). Higher ply ratings or load ranges signify greater load-carrying capability.

2.4 Tread Depth
Measured in 32nds of an inch or millimeters, tread depth affects traction, especially in wet conditions, and indicates the tire's remaining lifespan. OTR and agricultural tires have significantly deeper treads than passenger car tires.
III. Tire Industrial Clusters in China
China's tire manufacturing is heavily concentrated in specific regions, benefiting from industrial synergies, skilled labor, and established supply chains.

Shandong Province: This is the undisputed heartland of China's tire industry. Cities like Qingdao, Weifang, Dongying, and Zaozhuang are home to a vast number of tire manufacturers, ranging from global giants to smaller specialized producers. Shandong benefits from its proximity to rubber-producing regions and major ports, facilitating both raw material import and finished product export. It produces a full spectrum of tires, with a strong emphasis on TBR and OTR tires.
Zhejiang Province: While not as dominant as Shandong, Zhejiang also hosts significant tire manufacturing, particularly for passenger car and light truck tires, often at competitive price points.
Jiangsu Province: With its strong industrial base, Jiangsu also contributes to tire production, especially in the radial tire segment.
Other Regions: Other provinces like Liaoning and Anhui also have notable tire production facilities, often specialized in certain types or catering to specific domestic or international markets.

These clusters offer a comprehensive ecosystem for tire production, including raw material suppliers, machinery manufacturers, and logistics services, making them ideal sourcing locations.
IV. Domestic Major Tire Manufacturers (Leading Enterprises)
China boasts several world-class tire manufacturers that have gained significant market share globally, competing with established international brands. These companies have invested heavily in R&D, quality control, and advanced manufacturing technologies.
ZC Rubber (Zhongce Rubber Group Co., Ltd.): https://www.zc-rubber.com/ One of the largest tire manufacturers in China and globally, ZC Rubber produces a vast range of tires under popular brands like Westlake, Goodride, Chaoyang, Arisun, and Trazano. They cover PCR, TBR, OTR, and motorcycle tires, exporting to over 160 countries. ZC Rubber is known for its scale and OEM-grade reputation.
Sailun Group: https://en.sailungroup.com/ A leading player in tire R&D and automation, Sailun produces tires under brands like Sailun, RoadX, and Windpower. They are known for redefining mid-tier performance in PCR and TBR segments and have a strong export focus. Sailun also has overseas production bases.
Linglong Tire (Shandong Linglong Tire Co., Ltd.): https://en.linglong.cn/ A globally influential tire company with manufacturing bases in China, Thailand, and Serbia. Linglong supplies tires to major OEMs like Volkswagen, GM, and Ford, producing PCR, TBR, and OTR tires. They are known for their technological advancements and diverse product portfolio.
Triangle Tyre Co., Ltd.: https://www.triangle.com.cn/ Founded in 2001, Triangle Tyre is a global success with significant annual production. They are a major supplier of TBR and OTR tires and have received numerous quality awards from partners like Caterpillar. Their tires are certified by global quality standards (CCC, ECE, DOT, etc.).
Double Coin Holdings Ltd.: https://www.doublecoinholdings.com A subsidiary of Shanghai Huayi Group, Double Coin is a legacy brand with over 90 years in tire manufacturing, particularly renowned for high-performance TBR and OTR tires.
Aeolus Tyre Co., Ltd.: https://www.aeolus-tyres.com/ Founded in 1965, Aeolus is a powerhouse in commercial tires, especially in TBR, OTR, and agricultural categories.

Prinx Chengshan (Shandong Prinx Chengshan Tire Co., Ltd.): https://en.prinxchengshan.com/ Another significant player, offering PCR, SUV, and TBR tires, known for its strong technical specifications and export capabilities.
Qingdao Double Star Tire Industrial Co., Ltd.: https://www.doublestartyre.com/ Founded in 1921, headquartered in Qingdao, Doublestar is the only state-owned listed tire company in Shandong Province, as the world's first "Industry 4.0" Smart Tire Factory, offering PCR, SUV, and TBR tires, known for its green manufacturing technologies and high-tech and sustainable development.
- Giti Tire Co., Ltd.: https://www.giti.com/ A world-wide tire company with the main R&D center and production base in China, famous for its PCR, TBR, with good cost efficient.
Huasheng Tyre Co., Ltd.: https://www.hstyre.com A fast-growing company producing TBR and PCR tires, competitive in pricing and strong in African, Latin American, and Middle Eastern markets.
These manufacturers often operate multiple brands, catering to different market segments and price points, while adhering to international quality standards.
V. Relevant Certification Requirements
Ensuring that tires meet international and national safety and quality standards is paramount for successful import and market entry.

CCC (China Compulsory Certificate): This is a mandatory safety mark for both domestically manufactured and imported products sold within China. For automotive products, including tires, CCC certification is essential. The process involves product testing in China, an initial factory audit, and annual follow-up inspections. Without CCC, products cannot be legally imported, sold, or used in China.
DOT (Department of Transportation): Required for tires sold in the United States. DOT certification signifies that the tire manufacturer has certified that the tire meets U.S. safety standards. Each DOT-certified tire carries a specific code molded into its sidewall, indicating the manufacturing plant, tire size, and week of production.
ECE/E-Mark (Economic Commission for Europe): Mandatory for tires sold in the European Union and many other countries that adhere to ECE regulations. The E-Mark indicates that the tire complies with relevant UN Regulations regarding safety and environmental performance. Similar to DOT, an E-Mark on the sidewall signifies compliance.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): While not a product certification, ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) and ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949 for automotive quality management) are crucial certifications for the manufacturer's quality management processes. They indicate that the factory operates under a robust quality system, which is a strong indicator of product consistency and reliability.
GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council): Required for tires imported into GCC member states (Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE).
INMETRO: Mandatory certification for tires sold in Brazil.
SNI: Mandatory certification for tires sold in Indonesia.
Buyers must confirm that the Chinese manufacturer holds the necessary certifications for their target market to avoid customs issues and legal complications.
VI. Tire Purchasing Considerations
Sourcing tires from China can be highly beneficial, but a strategic approach is necessary to ensure quality, manage costs, and build reliable partnerships.

6.1 Defining Quality Standards
"Quality" is subjective. It's crucial for importers to explicitly define their quality requirements and product specifications (e.g., material composition, tread depth tolerances, expected performance metrics, specific testing standards) to the supplier. Provide detailed specifications, drawings, and any relevant industry standards you expect the tires to meet. Do not assume the manufacturer understands your market's specific quality expectations.
6.2 Manufacturer vs. Trading Company
Whenever possible, try to identify and deal directly with the original manufacturer rather than a trading company. Manufacturers generally offer better pricing, more transparent production processes, and greater control over customization and quality. While trading companies can simplify sourcing, they add a layer of cost and can sometimes obscure the true source of the product. Look for detailed quotes, professional responses to technical questions, and evidence of factory operations.

6.3 Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Chinese manufacturers typically have MOQs due to production line setup costs and economies of scale.
Negotiation: Always negotiate the MOQ. Suppliers may be open to "test orders" with lower quantities, especially for new relationships.
Product Variants: Inquire if you can combine different product variants (e.g., various sizes of the same tire model) to meet a higher overall MOQ.
Standard vs. Custom: Standard or slightly customized products usually have lower MOQs than entirely custom-designed tires.
Packaging: Simplified or standard packaging can sometimes reduce MOQ, as custom-printed packaging often has its own high MOQ.
Price Adjustment: Be prepared to pay a slightly higher unit price for a lower MOQ, as this helps the supplier cover their fixed costs for smaller runs.
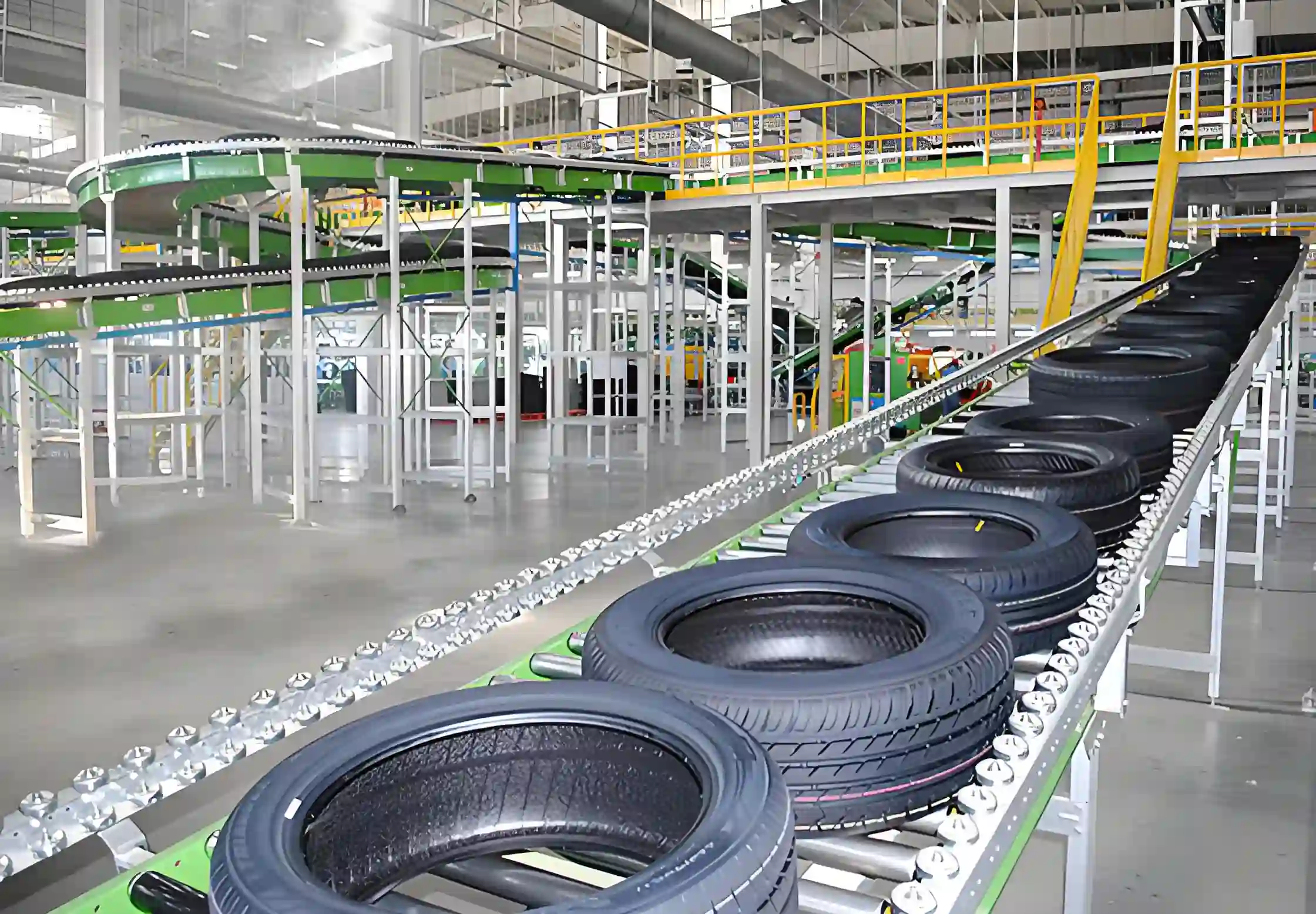
6.4 Quality Control (QC) and Inspections
Implementing robust QC measures is vital to mitigate risks and ensure product consistency.
Pre-Production Inspection: Verify raw materials and components meet specifications before mass production begins.
During Production Inspection (DPI): Monitor the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early.
Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): The most critical stage. A third-party inspection agency (or your own trusted representative) should conduct a thorough inspection of the finished goods before shipment. This check should cover:
Quantity and assortment verification.
Visual inspection for defects (paint peeling, deformation, uneven tread, sidewall blemishes).
Measurement of key parameters (tread depth, dimensions).
Verification of proper marking and labeling (including certification marks).
Packaging integrity.
Conducting or overseeing performance tests if required.
Relationship Building: Building a long-term, trustworthy relationship with your supplier can lead to more flexible terms and consistent quality. Frequent communication and clear expectations are key.
6.5 Customization Options
Chinese tire manufacturers are often highly flexible regarding customization.
Brand/Logo: Most manufacturers allow buyers to brand tires with their own logo or private label.
Tread Patterns: While developing entirely new patterns can be costly and have high MOQs, minor modifications or choosing from existing mold libraries is often possible.
Compound Formulation: Specific rubber compounds can be developed for desired performance characteristics (e.g., longevity, grip, fuel efficiency), though this usually requires larger volumes and significant R&D.
Color Strips/Markings: Aesthetic customizations like colored sidewall stripes or specific markings are common.
6.6 Shipping and Logistics
Sea Freight: The most common and cost-effective method for shipping tires from China, especially for large volumes. Tires are typically shipped in containers (20-foot or 40-foot, including high cubes).
Incoterms: Clearly define Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, EXW) with your supplier. This dictates who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk at various stages of the journey. For beginners, FOB (Free On Board) is often recommended, as the supplier handles local transport and loading onto the vessel at the port of origin.
Packaging: Tires are often shipped without individual packaging to optimize container space, but may be strapped or wrapped in bundles. For smaller quantities or specific requirements, individual wrapping or palletization can be arranged.
Partial Disassembly: For very large tires (e.g., OTR), partial disassembly might be employed to reduce shipping volume and cost.
6.7 Communication and Cultural Nuances
Effective communication is vital. While many Chinese suppliers have English-speaking sales teams, consider working with a local sourcing agent or representative who understands both the language and the business culture. WeChat is often the preferred communication method for quick exchanges in China. Be clear, concise, and persistent in your inquiries. Always get everything in writing.

VII. Choose IMEXsourcing as Your Sourcing Partner for Rubber Tire in China
When it comes to procuring high-quality rubber tire from China, partnering with an experienced and reliable sourcing agent is paramount. IMEXsourcing stands out as a premier choice, offering a comprehensive suite of services designed to streamline your acquisition process and secure exceptional value. Here are compelling reasons to select IMEXsourcing for your next purchase on tyre products:
Extensive Procurement Expertise
IMEXsourcing boasts a profound and long-standing history in the sourcing industry, enabling us to proficiently locate and secure a wide array of rubber tire from highly regarded Chinese suppliers. Our deep market knowledge ensures that we connect you with manufacturers known for their reliability and superior products.
Bespoke Design Solutions
At IMEXsourcing, we understand that unique requirements often demand tailored solutions. We empower you to commission well-designed and standard-produced tyre precisely engineered to your specifications, ensuring the final product perfectly aligns with your operational needs.
Thorough Supplier Verification
Our commitment to quality begins with rigorous due diligence. We conduct comprehensive factory verifications for all potential manufacturers. This meticulous audit confirms their production capabilities, assesses their quality control protocols, and ensures their full compliance with relevant industry standards and legal requirements.
Expert Price Negotiation
Leveraging our veteran status and in-depth understanding of the market dynamics, IMEXsourcing excels in negotiation. This invaluable expertise allows us to secure the most favorable pricing and terms with top-tier manufacturers renowned for their products, pattern, size and cost-efficient, optimizing your investment.
Stringent Quality Assurance
IMEXsourcing implements a robust quality management framework that spans the entire procurement cycle. This includes careful selection of suppliers, diligent oversight through production inspections, and thorough product testing prior to shipment, guaranteeing the integrity and performance of your equipment.

VIII. Conclusion
The Chinese tire industry offers a world of opportunity for global buyers seeking high-quality, cost-effective products across all categories. By thoroughly researching product types, understanding key specifications, identifying reputable manufacturers in established industrial clusters, ensuring adherence to vital international certifications, and implementing smart purchasing strategies—including clear quality control and effective communication—importers can successfully navigate the market and build profitable, long-term partnerships with Chinese tire suppliers.







