
Contents
I. Introduction: The “Climate-Controlled Cornerstone” of Modern Agriculture
In global agriculture and horticulture, greenhouses are indispensable infrastructure—ranging from small plastic film sheds for family farms to large-span glass greenhouses for commercial plantations and IoT-integrated intelligent multi-span greenhouses. Built with steel, glass, or PC panel structures and equipped with environmental control systems, they create stable growing conditions through light transmission, thermal insulation, and humidity regulation, underpinning continuous crop production and quality optimization.
China leads the global greenhouse production and export market. It boasts a complete industrial chain covering core components (steel frames, covering materials) to smart supporting systems (temperature control, irrigation, shading equipment). Large-scale manufacturing brings cost advantages, while upgraded technical standards—such as energy-saving insulation, IoT-based precision control, and eco-friendly materials—make Chinese greenhouses a top choice for global buyers. However, procurement requires attention to structural differences (single-span/multi-span), material specifications (glass/PC film thickness, steel frame corrosion resistance), and international certifications (ISO, CE) to mitigate supply risks.
This guide helps international buyers master key knowledge for sourcing from quality Chinese greenhouse manufacturers, enabling efficient supplier connection and access to high-performance, customized greenhouse solutions that meet diverse agricultural needs.
II. Main Application Scenarios of Greenhouses
1. Agricultural Production Scenarios
As the core application field of greenhouses, this category covers the entire crop planting chain and adapts to diverse geographical conditions and requirements:
- Off-season Crop Cultivation: Breaking through climatic constraints, it enables the planting of vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and green peppers in northern China during winter, and the cultivation of cold-tolerant vegetables (e.g., spinach, lettuce) in southern China during summer, ensuring the year-round supply of fruits and vegetables. In flower cultivation, it supports the winter growth of cut flowers like roses and lilies to meet the market demand throughout the year.
- Early-maturing/Late-maturing Crop Cultivation: In spring, greenhouses raise temperatures to advance the seedling cultivation of crops such as watermelons, strawberries, and eggplants. These seedlings are then transplanted to open fields when the external temperature is suitable, shortening the growth cycle and seizing market opportunities. In autumn, thermal insulation extends the crop growth period and delays the harvest time (e.g., late-maturing grapes and citrus fruits).
- Specialty Crop Cultivation: It is used for growing high-value-added medicinal plants (e.g., Dendrobium officinale, ginseng), tropical crops (e.g., pitayas, bananas in northern regions), edible fungi (e.g., shiitake mushrooms, enoki mushrooms with controlled humidity and light), as well as soilless crops including hydroponic vegetables and aeroponic lettuce.
- Seedling Propagation: It provides high-quality seedlings for open-field agriculture and horticulture, such as rice seedlings, vegetable seedlings, and fruit tree saplings. By controlling temperature and humidity inside greenhouses, the survival rate and growth consistency of seedlings are significantly improved.

2. Scientific Research and Experimental Scenarios
- Agricultural research institutions use greenhouses to build controlled experimental environments for conducting studies on crop variety improvement, pest and disease control, water and fertilizer management technologies, and the impacts of environmental stress (high temperature, low temperature, drought). These facilities eliminate interference from natural environments and ensure the acquisition of accurate experimental data.
- Relevant agricultural majors in universities utilize greenhouses for teaching practice, allowing students to intuitively understand crop growth patterns and protected agriculture operation techniques.
3. Tourism and Leisure Scenarios
Modern agricultural parks and eco-farms develop greenhouses into tourism and experience projects, such as picking gardens (for greenhouse-grown strawberries and cherry tomatoes), flower viewing greenhouses, and tropical plant pavilions. Combining agricultural experiences and popular science education, these projects promote the development of leisure agriculture and rural tourism.
4. Other Special Scenarios
- In some regions, greenhouses serve as auxiliary facilities for livestock and poultry breeding. For example, insulated greenhouses are built for chicks and piglets in winter to reduce cold stress. They are also applied in aquaculture to control water temperature for raising tropical fish, shrimps, crabs, etc.
- In cold northern regions, greenhouses are used for overwintering protection of seedlings, preventing frost damage and ensuring the survival rate of afforestation in the following year.
1. Core Energy Cycle: Temperature Regulation (Heat Preservation + Heating + Cooling)
Temperature is the most fundamental regulatory target of greenhouses, and dynamic balance is achieved through multiple structures and equipment:
- Passive Heat Preservation and Heating: Greenhouses are mainly constructed with transparent covering materials (glass, PC solar panels, plastic films). During the day, these materials can efficiently transmit short-wave solar radiation, allowing the ground, soil, and crops inside the greenhouse to absorb heat and warm up. At night, when heat is emitted in the form of long-wave radiation, the enclosed structure reduces heat convection. Combined with thermal insulation blankets/straw mats (used at night in winter), the heat inside the greenhouse is retained to prevent sudden temperature drops. Some greenhouses in northern regions also lay thermal insulation layers under the soil to avoid root damage caused by excessively low ground temperatures.
- Active Heating: In low-temperature seasons, auxiliary heating can be achieved through coal/gas-fired heaters, electric heating wires, or hot water pipe heating systems. Modern agricultural greenhouses are often equipped with geothermal systems, which utilize the constant temperature characteristics of the underground to provide a stable heat source. Others adopt biomass combustion furnaces, balancing environmental protection and heating needs.
- Active Cooling: During high-temperature summer, ventilation systems (roof vents + side vents) are used to form air convection and expel hot air. Shade nets are deployed to block part of the intense sunlight and heat, preventing crop scorching due to overheating inside the greenhouse. High-end greenhouses are installed with pad-fan cooling systems, which realize rapid cooling by absorbing heat through water evaporation.
2. Light Management: Maximizing Natural Light + Artificial Supplement
Light is the energy source for crop photosynthesis. Greenhouses optimize light conditions through structural design and auxiliary equipment:
- Efficient Utilization of Natural Light: Most greenhouses adopt arch/ sloped structures and are oriented north-south (in the Northern Hemisphere) to ensure crops receive uniform sunlight, reducing shadow coverage. Transparent covering materials with high light transmittance are selected, and surface dust and snow are regularly cleaned to avoid affecting light penetration.
- Artificial Light Supplement: In winter with short daylight hours or rainy and cloudy weather, LED grow lights, high-pressure sodium lamps and other equipment are used for supplementary lighting. This extends the photosynthesis duration of crops and promotes their growth and development. The light spectrum of supplementary lamps can be adjusted according to crop types (e.g., leafy vegetables require mainly blue light, while fruit vegetables need primarily red light).

3. Humidity and Ventilation: Regulating Air Humidity to Prevent Pests and Diseases
High humidity is prone to occur in enclosed environments, leading to crop diseases. Thus, humidity needs to be regulated through ventilation and humidity control equipment:
- Natural Ventilation: By opening roof and side vents, air convection is formed relying on temperature differences and wind power between inside and outside the greenhouse. This expels high-humidity air and introduces dry external air to reduce humidity.
- Forced Ventilation: In large-scale greenhouses or windless weather, circulation fans are activated to accelerate air flow inside the greenhouse, avoiding local excessive humidity. Dehumidifiers (equipped in high-end greenhouses) are used for precise humidity control.
- Humidity Utilization: For humidity-loving crops (such as strawberries and lettuce), spray systems can be used to increase air humidity and meet their growth requirements. Meanwhile, appropriate humidity reduces crop water evaporation, saving irrigation water.
4. Water and Fertilizer Management: Precise Supply to Improve Resource Utilization
Most greenhouses are equipped with water-saving irrigation and precision fertilization systems, which avoid water and fertilizer waste in traditional planting and meet the needs of crops at different growth stages:
- Irrigation Methods: Common systems include drip irrigation and micro-sprinkler irrigation, which deliver water directly to the vicinity of crop roots, reducing evaporation and seepage. Some greenhouses are installed with ebb and flow irrigation systems, allowing crop roots to fully absorb water and nutrients through periodic water rise and fall.
- Integration of Water and Fertilizer: Fertilizers are dissolved in irrigation water and accurately delivered to crop roots through pipelines, realizing “fertilization while irrigation.” This not only saves fertilizer consumption but also prevents soil compaction and improves crop absorption efficiency. Some systems can automatically adjust the water-fertilizer ratio based on crop growth data.
5. Other Auxiliary Systems (Modern Agricultural Greenhouses)
With technological advancement, high-end greenhouses integrate more intelligent systems to achieve automated and precise management:
- Intelligent Control Systems: Sensors are used to real-time monitor data such as temperature, humidity, light, CO₂ concentration, and soil moisture inside the greenhouse. Computers or mobile apps automatically control the operation of ventilation, irrigation, light supplement, fertilization and other equipment, reducing manual intervention.
- CO₂ Fertilization Systems: In enclosed environments, crop photosynthesis consumes a large amount of CO₂, resulting in reduced concentration. CO₂ generators (e.g., natural gas or biomass combustion) are used to supplement CO₂, improving crop photosynthesis efficiency and increasing yield.
- Insect Screens and Pest Control: Insect screens are installed at greenhouse entrances and vents to physically block pests from entering. Combined with green prevention and control equipment such as sticky traps and insect-killing lamps, pesticide use is reduced, achieving green planting.
IV.How to Choose a Greenhouse?
Selecting export – oriented greenhouses requires focusing on core needs (crop types, target country’s environment, budget costs, technical adaptability), and making comprehensive decisions based on the product’s structural strength, weather resistance, operational convenience, and the industry standards of the target market. Below is a systematic selection framework and practical recommendations:
V. How to Find Greenhouse Suppliers in China?
VI. What are the Production Bases of Greenhouses?
VII. Major Domestic Manufacturers of Greenhouses in China
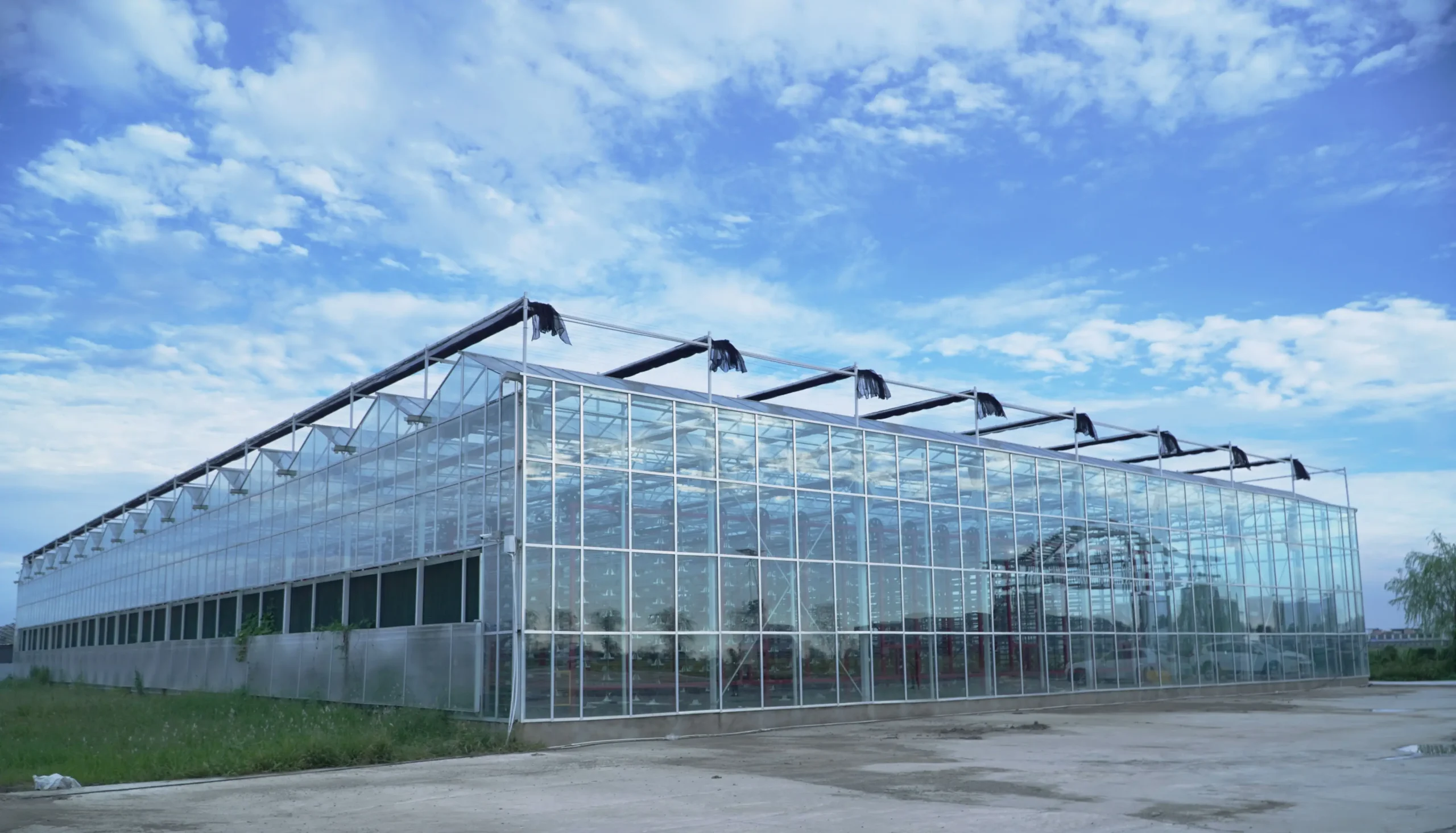
1. Chengdu Chengfei Green Environment Technology Co., Ltd.
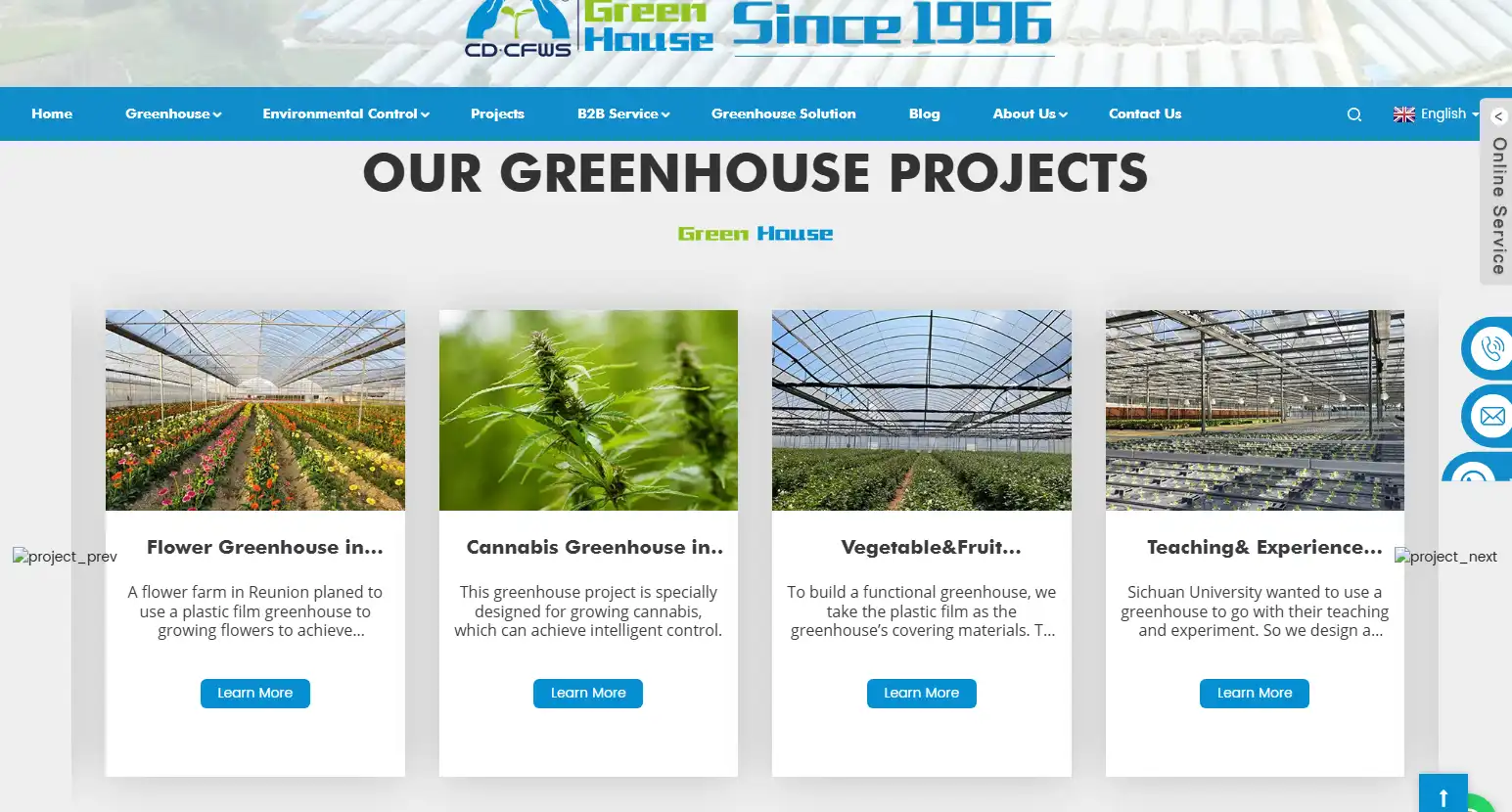
Since its inception in 1996, Chengfei Greenhouse has provided a full range of greenhouse services for global customers and gained wide recognition for its quality solutions and services.
2.Qingzhou Luyuan Greenhouse & Horticulture Engineering Co., Ltd.
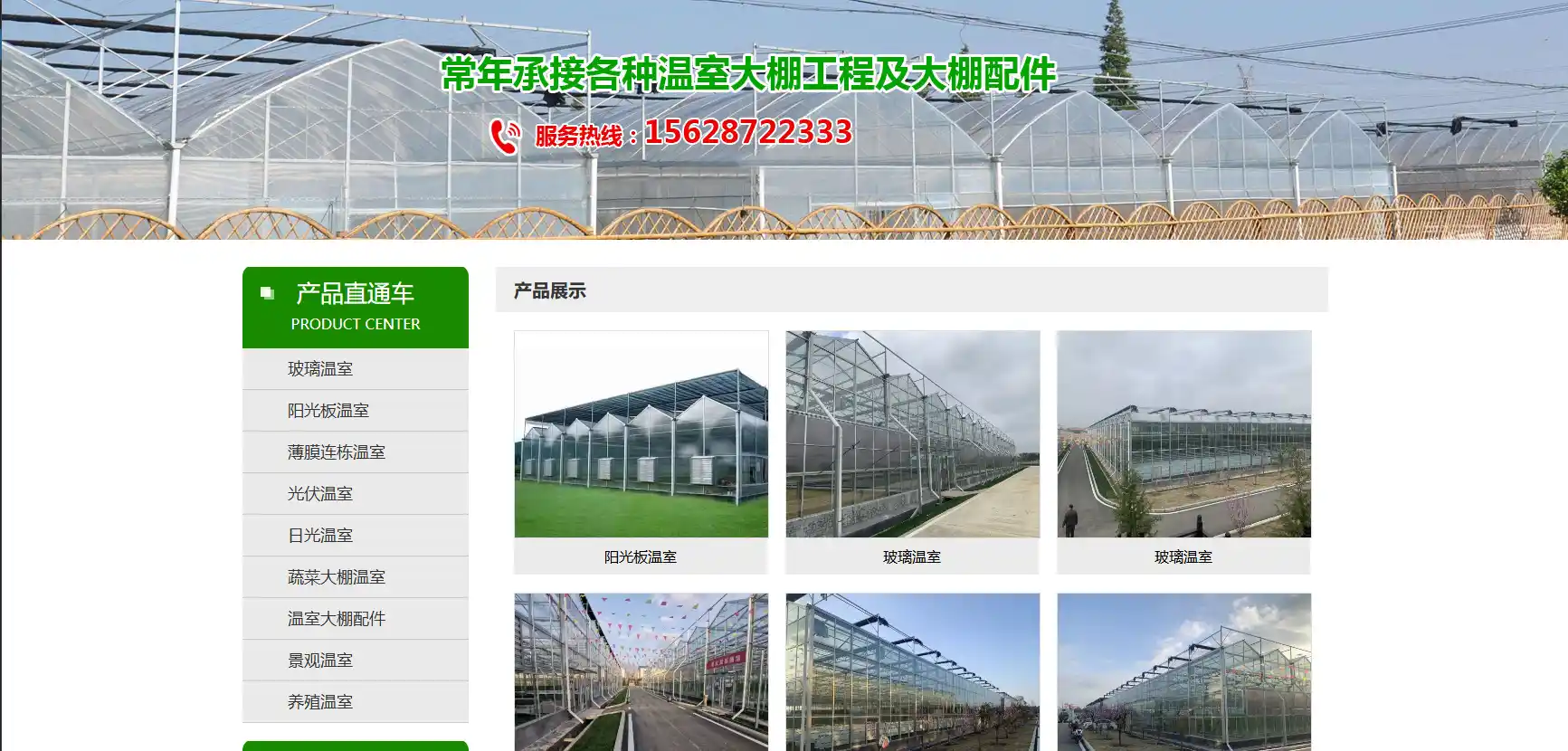
A core manufacturer in Qingzhou, offering glass/PC multi-span greenhouses, photovoltaic greenhouses with irrigation and temperature control, ideal for flowers, vegetables and seedling raising.
3.Foshan Kunyu Greenhouse Engineering Co., Ltd.
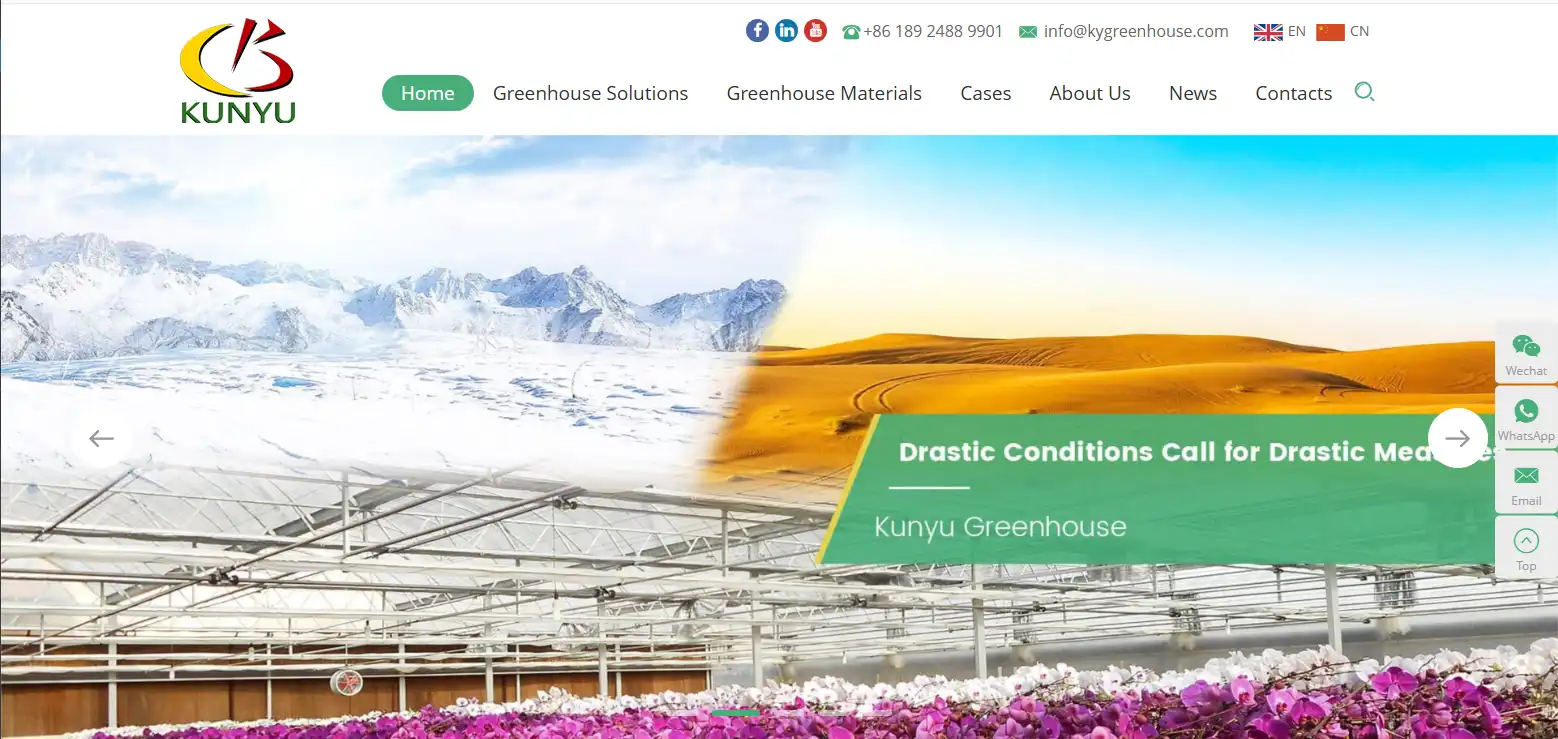
A benchmark for high-value flower greenhouses in South China, specializing in phalaenopsis-specific greenhouses with precise environmental control, suitable for high-temperature, high-humidity and typhoon-prone climates.
4. Sichuan Chenchao Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd.

A leading greenhouse enterprise in Southwest China, offering film multi-span greenhouses, solar greenhouses and seedling facilities, with rich construction experience adapting to mountainous climates in Southwest China.
5. Qingzhou Huade Agricultural Equipment Co., Ltd

Covers Venlo-type glass, PC, film multi-span and solar greenhouses; customizes ecological restaurants and photovoltaic greenhouses.
6.Qingzhou Shine Tech Agriculture Equipment Co.,LTD
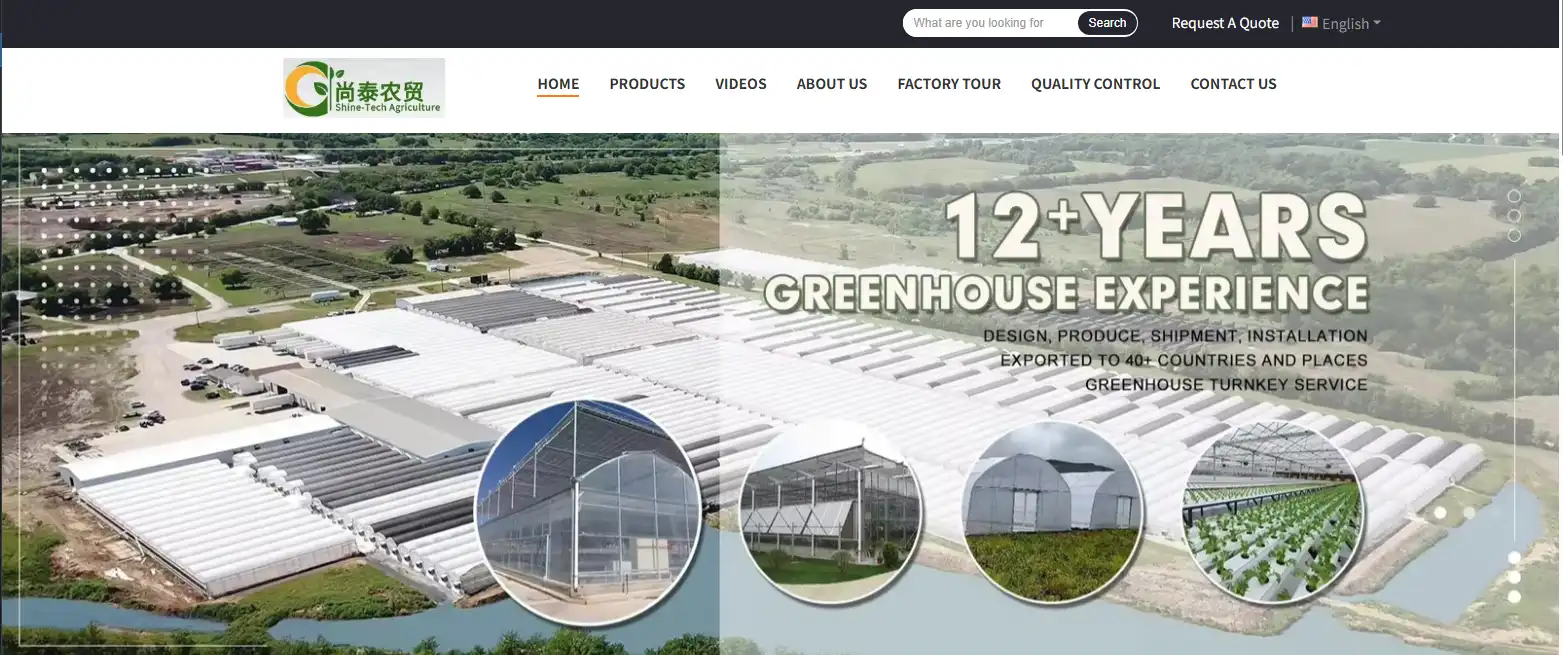
Main products are single tunnel greenhouse,multi span film greenhouse,polycarbonate greenhouse,Venlo glass greenhouse,Photovoltaic greenhouse,winter solar
greenhouse,blackout greenhouse,hydroponic system, greenhouse film,cooling fan and pad,shading system, heating system,nursery bench,etc.
7. Weifang Sainpoly Greenhouse Equipment Co., Ltd.

Covers Venlo-type glass, PC, film multi-span and solar greenhouses; customizes ecological restaurants and photovoltaic greenhouses, serving provinces nationwide.
VIII. Precautions for Purchasing Greenhouses: A Guide to Informed Decisions
After identifying potential greenhouse suppliers and their products, follow these steps to ensure a smooth procurement process:
- Request samples or site visits first: Always ask for structural samples (e.g., frame materials, covering films/panels) or arrange site visits to existing projects before placing bulk orders. Check core quality such as frame load-bearing capacity, covering material lighttransmittance/insulation, joint firmness, and corrosion resistance, while confirming that structural specifications and accessory configurations meet your planting needs.
- Evaluate production and customization capabilities: Inquire about the supplier’s daily/monthly production capacity of greenhouse components and overall installation cycles to ensure they can fulfill bulk or customized orders (e.g., special spans, climate-adapted designs). Confirm consistency in material quality across batches (e.g., no differences in steel frame thickness or film UV resistance).
- Consider after-sales support: Confirm the supplier offers after-sales guarantees such as on-site maintenance for structural failures, replacement of damaged parts during transportation, and technical guidance for installation and operation. For intelligent greenhouses, clarify the warranty period for control systems and the availability of troubleshooting services.
- Calculate total costs: Beyond the unit price of the greenhouse, include costs for auxiliary equipment (e.g., irrigation, temperature control systems), transportation fees for bulk components, on-site installation labor costs, and additional expenses for customization (e.g., anti-typhoon reinforcement, intelligent sensor integration).
- Verify qualifications and certifications: Use third-party inspection services or platform certifications to check if the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, agricultural facility production licenses) and if materials meet safety and environmental standards (e.g., non-toxic and pollution-free covering films, corrosion-resistant and durable steel frames).
IX. Choose IMEXsourcing as Your Greenhouse Sourcing Partner in China
When procuring high-quality greenhouses and related equipment from China, partnering with an experienced and reliable sourcing agent is crucial. IMEXsourcing stands out with a comprehensive service suite to streamline your procurement process and secure exceptional value, with core advantages as follows:
- Extensive procurement expertise: With years of experience in the greenhouse sourcing industry, we accurately connect you with top Chinese suppliers, covering a full range of products including intelligent glass multi-span greenhouses, solar greenhouses, film arch sheds, and matching equipment (irrigation systems, temperature control devices) to meet diverse procurement needs for different crops and climates.
- Bespoke solutions: We support customization based on your requirements, including greenhouse span/size, covering material selection (glass/PC board/anti-UV film), climate-adapted designs (anti-typhoon/insulation reinforcement), and intelligent system configuration (IoT monitoring, automatic water-fertilizer integration), perfectly aligning with your planting scale, crop types and regional environmental characteristics.
- Strict supplier verification: We conduct comprehensive factory audits on cooperative manufacturers, verifying production capacity, structural design capabilities and quality control processes to ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, agricultural facility production licenses) and products meet domestic and international safety and performance standards (load-bearing capacity, light transmittance).
- Professional negotiation capabilities: Leveraging industry resources and aggregated procurement volume, we secure the most favorable pricing and terms for you, minimizing procurement costs while avoiding hidden expenses such as substandard materials or delayed delivery.
- Full-cycle quality assurance: We implement a robust end-to-end quality management system, including sample confirmation, production process supervision, and pre-shipment inspection (verifying core indicators such as frame firmness, covering material performance, and accessory completeness), ensuring stable quality of delivered greenhouses and equipment.
X. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Chinese greenhouse market offers abundant opportunities for global buyers. By carefully researching product categories (from cost-effective film arch sheds to high-end intelligent glass multi-span greenhouses, cold-resistant solar greenhouses, and crop-specific custom facilities), clarifying technical parameters (such as structural load-bearing standards, climate-adapted configurations for diverse regions, and requirements for light transmittance and thermal insulation), and following a systematic procurement process, importers can source high-quality, cost-effective greenhouses to meet diverse market demands—whether for commercial crop cultivation, agricultural park development, or high-value flower planting needs.
Partnering with IMEXsourcing provides solid protection for your procurement journey. We understand that the greenhouse industry involves complex structural manufacturing and multi-system integration, and some factories may face operational instability risks, leading to issues like order delays, substandard component quality, and advance payment losses. Additionally, IMEXsourcing boasts a strategic location, just a 1-hour drive from Qingzhou, Shandong—the largest core greenhouse production base in China—enabling quick on-site inspections and real-time production supervision. Through on-site verification, we confirm factories’ actual operating status (e.g., equipment advancement, engineering team professionalism), financial health (e.g., potential cash flow risks), and past performance records (e.g., project completion timeliness), helping you screen high-quality manufacturers with stable operations and strong risk resistance from the source, and completely avoiding financial losses and procurement disruptions caused by factory operational problems.