Índice
ToggleI. Product Type Introduction: A World of Mud Pumps
1. Reciprocating Mud Pump
- Piston Mud Pump: It relies on the reciprocating motion of the piston in the pump cylinder and seals the pump chamber with piston rings. Suitable for conveying mud with a small amount of solid particles, it is often used in medium-deep well drilling (e.g., well depth of 2000-4000 meters) and features high cost-effectiveness and low maintenance costs.
- Plunger Mud Pump: It uses plungers (without piston rings, relying on packing for sealing) instead of pistons. It has stronger sealing performance and more outstanding high-pressure resistance (working pressure can reach 35-70MPa), and can convey high-viscosity mud with a large amount of solid particles. It is the mainstream choice for deep wells, ultra-deep wells (>4000 meters), and shale gas horizontal well drilling. However, it has slightly higher requirements for mud cleanliness and needs to be equipped with a high-efficiency filtration system.
2. Centrifugal Pump
- Pre-treatment of drilling fluid (e.g., stirring in the mud tank, conveying to the suction end of the main mud pump);
- Drilling of shallow small-boreholes (e.g., exploration wells with a depth of <1000 meters), or as a supporting conveying equipment for solid control systems.
3. Screw Pump
- Conveying special mud with high viscosity and high solid content (e.g., drilling fluid containing weighting agents);
- Mud recovery systems on offshore drilling platforms. Due to its small size and small floor space, it is suitable for the limited space of platforms. However, its high-pressure resistance is weak (working pressure is usually <10MPa), so it is not suitable for the main circulation of deep wells.
II. The Working Principle of a Mud Pump
A mud pump, primarily referring to the reciprocating mud pump widely used in drilling operations, operates on the principle of positive displacement. It converts mechanical energy into the pressure energy of the mud through the reciprocating motion of pistons or plungers, facilitating the continuous transportation of mud (drilling fluid) to the drilling well. The specific steps are as follows:
Suction Stroke:
When the power end (driven by a motor) drives the crankshaft to rotate, the connecting rod pulls the piston/plunger to move backward in the cylinder. This creates a negative pressure zone inside the cylinder. Under the action of atmospheric pressure, the mud in the suction tank pushes open the suction valve (a one-way valve) and enters the cylinder cavity, completing the suction process.
1. Discharge Stroke
As the crankshaft continues to rotate, the connecting rod pushes the piston/plunger to move forward in the cylinder. The mud in the cylinder is compressed, and the pressure rises rapidly. When the pressure exceeds the pressure of the discharge pipeline, the discharge valve (another one-way valve) is pushed open, and the high-pressure mud is discharged into the pipeline and transported to the drilling well or related equipment (e.g., desanders, drill bits).
2. Continuous Operation
With the continuous rotation of the crankshaft, the piston/plunger alternately performs “suction stroke” and “discharge stroke.” The suction valve and discharge valve open and close alternately (controlled by pressure differences) to ensure that mud is continuously sucked into the cylinder and discharged at high pressure, realizing the stable circulation of drilling fluid in the drilling system.
Key Term Explanations
· Reciprocating Mud Pump: The most common type of mud pump, characterized by the reciprocating motion of pistons/plungers, suitable for conveying high-pressure, high-solid-content mud.
· Positive Displacement Principle: The pump delivers fluid by changing the volume of the working cavity (cylinder) to push the fluid forward, ensuring stable discharge pressure even with changes in pipeline resistance.
· Suction/Discharge Valves: One-way valves that prevent mud backflow, critical for maintaining the direction of fluid flow during suction and discharge strokes.
III. A Detailed Introduction to a Mud Pump

High Pressure Mud Pump (TSC Work Force Series)
1. Description
2. Features
- Compact footprint with a high horsepower-to-weight ratio
- Bearings and gearing engineered for a minimum L10 service life of 30,000 hours under rated load
- Rigid, fabricated oilfield-style frame and skid, providing a stable operating platform
- Fabricated crankshaft with a forged core to reduce vibration and ensure long-term durability
- Cast crossheads and guides for maximum service life
- Standard valve-over-valve, 5000 psi fluid ends (PZ8/9 style)
3. Performance Criteria
|
Parameter
|
Specification
|
|
Nominal Input Horsepower
|
700 HP (522 kW)
|
|
Maximum Strokes per Minute
|
150
|
|
Stroke
|
8.5 inches (215.9 mm)
|
|
Maximum Piston Diameter & Pressure
|
7 inches (177.8 mm) @ 1695 PSI
|
|
Minimum Piston Diameter & Pressure
|
4 inches (101.6 mm) @ 5000 PSI **
|
|
Suction Manifold
|
8 inches (203.2 mm) with 150 # flanges
|
|
Discharge Manifold
|
4 inches (101.6 mm) with 5000 PSI RJ flanges
|
|
Estimated Dry Weight
|
19,000 pounds (8600 kg) ^^
|
|
Oil Capacity
|
55 gallons (208 litres)
|
|
Gear Ratio
|
5.05:1
|
|
Compliance
|
API standard expendables
|
WF700 Typical Performance Characteristi
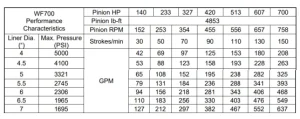
Notes:
- All data is subject to change without notice.
- All data is based on 100% or continuous duty cycle.
- Data is based on 90% mechanical and 100% volumetric efficiency.
- Achievable pressure will be limited by the horsepower available or the pressure
- limitations of the module used.
WF700 Typical Arrangement Drawing:
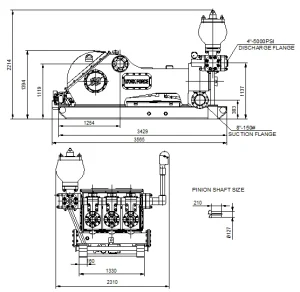
NOTE: Dimensions are approximate & subject to change; shown with standard accessories.
Standard Accessories:
• One 10 gallon pulsation dampener with strainer cross
• Pressure relief valve
• Pressure gauge
• Complete electrical lube & liner wash system
Optional Accessories:
• Charge pump
• Custom skids
• Motor starter(s) in explosion proof enclosure
• Dual lubrication pump
• Dual liner wash pump
• Custom drive unitization
• Jib crane
IV. Mud Pump Spare Parts List and Part Numbers
| No | Qty | NOV Part No | TSC part # | Description | materials |
| 1* | 1 | See below | See below | Casing | Hard Iron |
| 1A | 1 | 10399-46-1 | TS-10399-46-1 | Gasket, Casing | Vellumoid |
| 1B | 12 | 3932-61 | TS-3932-61 | Nut,Casing | Stl |
| 1C | 12 | 3862-76 | TS-3862-76 | Stud,Casing | Stl |
| 1D | 1 | 8505-4-1 | TS-8505-04-01 | Plug, Casing Drain | StI |
| 1E | 1 | 8505-4-1 | TS-8505-04-01 | Plug, Flush Line | Iron |
| 2* | 1 | See below | See below | Impeller | Hard Iron |
| 2A | 1 | 19110-72 | TS-19110-72 | Seal, Impeller | Viton |
| 2B | 1 | TS-7300239 | Washer, Impeller | Stl | |
| 2C | 1 | TS-7415648 | Bolt, Impeller Lock | Sd | |
| 3* | 1 | 22223-01-30 | TS-22223-01-30 | Stuffing Box, Mech.Seal | Hard lorn |
| 3* | 1 | 20614-01-30 | TS-20614-01-30 | Stuffing Box, Packed | Hard lorn |
| 3A | 2 | 3861-117 | TS-3861-117 | Bolt, Stuffing Box | Stl |
| 3B | 1 | 19368-01 | TS-19368-01 | Grease Fitting | Bronze |
| 4 | 1 | 20622A | TS-20622A | Gland Assy.,Packing | Bronze |
| 5 | 1 | 22451-1 | TS-22451-1 | Scal, Mechanical | Tungsten Carbide |
| 5A | 1 | 25014-04M-B | TS-25014-04M-B | Packing,Shaft | Kevlar |
| 6 | 2 | B3701A | TS-B3701A | Bolt Assy, Gland | Stl |
| 7 | 1 | TS-20612-02-33-S | shaft | AISI 4140 | |
| 7A | 1 | 20943-21 | TS-20943-21 | Sleeve,Shaft (M.S. Pump) | AISI E7140 |
| 7A | 1 | 20613-21G-7A | TS-20613-21G-7A | Sleeve, Shaft (Pack Pump) | AISI E7140 |
| 7B | 1 | 4372-5-21 | TS-4372-5-21 | Key,Shaft | 416SS |
| 7C | 1 | 23444-01-72 | TS-23444-01-72 | Seal,Shaft Sleeve | Viton |
| 8 | 1 | 22210-1A | TS-22210-1A | Deflector Assembly | Bronze |
| 9 | 1 | 20938-02-01 | TS-20938-02-01 | frame | Cast Iron |
| 9A | N/A | ||||
| 9B | N/A | ||||
| 9C | 1 | 8505-05 | TS-8505-05 | Plug,Oil Drain | Iron |
| 9D | 1 | 8267-01 | TS-8267-01 | Breather | Stl |
| 9E | N/A | ||||
| 9F | 1 | JB/T9740.3-1995 | Oil cupa B18 | A1 | |
| 9G | 3 | 2538-1H | TS-2538-1H | Bolt, casing jack | Stl |
| 10A | 1 | 20626 | TS-20626 | Cover,Inboard Bearing | Iron |
| 10B | 1 | 20625 | TS-20625 | Gasket, I.B. Bearing Cover | Vegetable Fiber |
| 10C | 1 | 20619-01 | TS-20619-01 | Oil Seal, I.B. Bearing Cover | Buna-n |
| 10D | 2 | 3861-1 | TS-3861-1 | Bolt, LB.Bearing Cover | Stl |
| 10E | 2 | 3932-2 | TS-3932-2 | Nut, I.B.Brg. Cover | Stl |
| 10F | N/A | ||||
| 10G | 1 | 21641-01 | TS-21641-01 | Grease Fitting | Stl |
| 11 | 1 | N/A | TS-661009010 | Bearing,Inboard | Vendor |
| 12 | 1 | 22224-01-43 | TS-22224-01-43 | Hydraulic Bearing Housing | Stl |
| 12A | 1 | 7496-253 | TS-7496-253 | Seal, O.B. Bearing Housing | Buna-n |
| 13 | 1 | 20617-01-01 | TS-20617-01-01 | Cover, O.B. Bearing | Iron |
| 13A | 1 | TS-661010020 | Grease Zerk, O.B. Bearing Cvr. | Stl | |
| 13B | 1 | 7496-26 | TS-7496-26 | O-ring, O.B. Bearing Cover | Buna-n |
| 13C | 1 | 20619-02 | TS-20619-02 | Oil Seal, O.B. Bearing Cover | Buna-n |
| 13D | 2 | 3861-139 | TS-3861-139 | Bolt, O.B. Bearing Cover | Stl |
| 14 | 1 | N/A | TS-648408201S | Bearing, O.B.(2 Req’d) | Vendor |
| 14A | 1 | 6124-4 | TS-6124-4 | Lockwasher, O.B. Bearing | Stl |
| 14B | 1 | 6123-4 | TS-6123-4 | Locknut, O.B. Bearing | Stl |
| 15 | 1 | 22225-01-01 | TS-22225-01-01 | Hydraulic Motor Adapter | Stl |
| 15A | 1 | N/A | TS-2273-1 | Spacer, Hydraulic Motor | Stl |
| 15B | 1 | N/A | TS-HDAGUARDS | Guards, Hydraulic Drive Adapter | 304 |
| 15C | 2 | N/A | Bolt, Adapter Guards | Stl | |
| 15D | 8 | N/A | Bolt, Adapter Spacer | Stl | |
| Casing | |||||
| 1* | 1 | 19203-01-30A | TS-19203-01-30A | Casing,3x2x13 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19205-01-30A | TS-19205-01-30A | Casing,4x3x13 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19222-01-30A | TS-19222-01-30A | Casing,5x4x11 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19122-01-30A | TS-19122-01-30A | Casing,6x5x11 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19123-01-30A | TS-19123-01-30A | Casing,6x5x14 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19763-01-30A | TS-19763-01-30A | Casing,8x6x11 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 19117-01-30A | TS-19117-01-30A | Casing,8x6x14 | Hard Iron |
| 1* | 1 | 20937-01-30A | TS-20937-01-30A | Casing,10x8x14 | Hard Iron |
| Impeller | |||||
| 2* | 1 | 19204-XX-30 | TS-19204-XX-30 | Impeller,3x2x13 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19206-XX-30 | TS-19206-XX-30 | Impeller,4x3x13 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19224-XX-30 | TS-19224-XX-30 | Impeller,5x4x14 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19121-XX-30 | TS-19121-XX-30 | Impeller,6x5x11 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19121-XX-30 | TS-19121-XX-30 | Impeller,6x5x14 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19121-XX-30 | TS-19121-XX-30 | Impeller,8x6x11 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 19116-XX-30 | TS-19116-XX-30 | Impeller,8x6x14 | Hard Iron |
| 2* | 1 | 21867-XX-30 | TS-21867-XX-30 | Impeller,10x8x14 | Hard Iron |
V. Domestic Major Manufacturers (Leading Enterprises)
- CM Energy Tech Co., Ltd.Founded in 1995, the company is listed on the Main Board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (Stock Code: HK00206). As a well-known provider in the field of oil and gas drilling & production equipment as well as marine supporting equipment, it boasts comprehensive capabilities in design, manufacturing and engineering services. The mud pumps produced by the company are of world-class standard.

- Shandong Rongli Petroleum Machinery Co., Ltd. Founded in 2002, it is an enterprise specialized in manufacturing petroleum drilling and production equipment such as drilling rigs and mud pumps. The company has independent technological R&D capabilities and has obtained 24 national patents. Its main products include petroleum drilling rigs, single mud pumps, mud pump units, diaphragm pumps, etc., which are widely used in various fields such as onshore petroleum drilling platforms and offshore petroleum drilling platforms.
- Qingdao Kehua Petroleum Machinery Co., Ltd. It has focused on petroleum drilling mud pumps and pump hydraulic end accessories for 22 years, and can provide oilfield well teams with a variety of mud pumps and accessories, such as the Baoshi F Series and Lanshi 3NB Series.
- Shengli Oilfield Gubang Petroleum Equipment Co., Ltd.The company has a broad business scope, covering the production and sales of various products such as mechanical processing, metal structural parts, solid control equipment and mud pumps, as well as services including the leasing and maintenance of drilling and production equipment.
VI. Relevant Certification Requirements
-
Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) CU-TR Certification: Most petroleum machinery falls into the high-risk product category under the EAEU CU-TR certification system and thus requires the application for a CU-TR Certificate of Conformity (COC). Examples include drilling rigs, high-pressure oil pipelines, and explosion-proof motors, which are subject to technical regulations such as TR CU 010/2011 “Safety of Machinery and Equipment”, TR CU 012/2011 “Safety of Explosion-Proof Equipment”, and TR CU 032/2013 “Safety of Equipment Operating Under Overpressure”. The certification process involves full-scale testing by an EAEU-accredited laboratory, as well as on-site factory audits and annual supervision audits. Only a small number of low-risk auxiliary equipment (e.g., manual wrenches, oil drum brackets) are eligible for the CU-TR Declaration of Conformity (DOC), which can be obtained through document review, self-declaration of compliance by the enterprise, and registration.
-
Uzbekistan GOST-UZ Certification: GOST-UZ is Uzbekistan’s mandatory certification system, and petroleum machinery is generally within the scope of mandatory certification. The certification process involves confirming the product classification and HS code, selecting a certification model (e.g., type approval or single-batch certification), and submitting application forms, technical documents, test reports, and the manufacturer’s ISO 9001 certificate. Samples must undergo testing in a Uzbekistan-accredited laboratory, and factory audits are required for type approval. Certificates are typically valid for 1–3 years, while single-batch certification is only valid for the specific import consignment.
-
Ukraine UkrSEPRO Certification: Ukraine’s UkrSEPRO Certification (formerly GOST-U Certification) is a mandatory certification system for petroleum machinery and other products to enter the Ukrainian market. The process involves determining the certification scheme (e.g., single-batch certification or serial production certification), preparing technical documents such as product technical passports, design drawings, and user manuals (which must be translated into Ukrainian and notarized). Samples need to be tested in a Ukraine-accredited laboratory, and factory audits are required for serial production certification. Certificates are valid for 1–3 years.
-
EU CE Certification: CE Certification is a mandatory requirement for petroleum machinery to enter the EU market. For petroleum machinery, it may be subject to directives such as the Low Voltage Directive (LVD), Machinery Directive (MD), and ATEX Directive (Explosion Protection Directive). For instance, electrical components of petroleum machinery must comply with the LVD to ensure electrical safety under normal use and fault conditions; mechanical parts must meet the MD to guarantee safety in design, manufacturing, and installation; and if the equipment is used in environments with potential explosive gases, it must adhere to the ATEX Directive.
-
US API Certification: Standards and certifications developed by the American Petroleum Institute (API) are widely recognized in the global petroleum industry. API certifications include API Spec 4F (Drilling Structures), API Spec 7K (Rotary Drilling Equipment), and API Spec 16A (Drilling Choke and Kill Equipment). Obtaining API certification indicates that petroleum machinery products meet the quality, performance, and safety standards specified by API, which helps enhance the product’s competitiveness in the international market—especially in the United States and other countries/regions that follow API standards.