Introduction to Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber (CF) is a special material composed of carbon elements. Its carbon content usually exceeds 90%, and it has excellent mechanical properties such as being lightweight, high-strength, high-modulus, temperature-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and fatigue-resistant.
The production of carbon fiber generally involves two main steps:
-
Precursor Filament Production: Using polyacrylonitrile (PAN), pitch, rayon, or phenolic resins as precursors, a continuous filament is produced through a spinning process.
-
Carbonization: The precursor filament is subjected to high-temperature pre-oxidation and carbonization in an oxygen-free environment, transforming it into a high-purity carbon fiber.
Carbon fiber is typically used in the form of tow, fabric, felt, chopped fibers, or prepregs. It is often combined with a resin matrix (like epoxy resin) to form Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRPs), which are widely used in aerospace, automotive, sporting goods, wind power, and construction industries.

Table of Contents
I. Classification of Carbon Fiber
There are many ways to classify carbon fibers. Here are a few common methods:
1. By Mechanical Properties
This is the most common classification method, based on the carbon fiber’s tensile strength and tensile modulus.
-
High-Strength (HS) Carbon Fiber: High tensile strength but relatively low modulus. It’s often used in applications requiring high strength, such as aerospace structural components and high-pressure vessels.
-
High-Modulus (HM) Carbon Fiber: High tensile modulus but relatively low strength. It’s often used in applications requiring high rigidity, such as satellite skeletons, optical instruments, and golf club shafts.
-
High-Strength and High-Modulus (HSHM) Carbon Fiber: Possesses both high strength and high modulus. This type of carbon fiber has a balanced performance and is a key direction for future development.

2. By Precursor Material
Based on the precursor (raw filament) used to produce the carbon fiber, it can be classified as:
-
Polyacrylonitrile-based (PAN-based) Carbon Fiber: This is the most widely produced and used type of carbon fiber. Its production process is relatively mature, and it offers excellent performance.

-
Pitch-based Carbon Fiber: Made from petroleum or coal tar pitch. This type of carbon fiber usually has a very high modulus but relatively lower strength.
-
Rayon-based Carbon Fiber: Made from rayon fiber, this type is now less commonly used.
-
Phenolic-based Carbon Fiber: Made from phenolic resin, this type of carbon fiber has excellent high-temperature resistance and ablation resistance.
3. By Form
Based on the form in which the carbon fiber is used, it can be classified as:
-
Continuous Filament: In the form of a continuous strand, typically used for weaving or filament winding to create structural components.

-
Chopped Fiber: Continuous carbon fibers are cut into short lengths, often used to reinforce plastics, concrete, etc.
-
Carbon Fiber Fabric: Continuous carbon fibers are woven into a cloth-like material for easier layering and composite molding.
-
Carbon Fiber Mat: A non-woven mat of randomly oriented fibers, often used for non-structural or filler applications.
II. Multifunctional Advantages: Why Chinese Carbon Fiber Stands Out
The Chinese carbon fiber industry has been developing rapidly in recent years, demonstrating unique advantages in technology, cost, and market aspects. Here are some key advantages of Chinese carbon fiber:
1. Complete Industrial Chain and Large-Scale Production
China has established a complete industrial chain, from precursor fibers and prepregs to finished carbon fiber products and composite material applications. According to data from Carbon Fiber Circular (CCF), the total carbon fiber capacity in mainland China exceeded 160,000 tons in 2023, accounting for half of the global capacity. The actual production reached 97,600 tons, an increase of 41.3% year-on-year. This large-scale production capacity ensures a more stable supply of carbon fiber products, meeting the growing market demand.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to some traditional carbon fiber-producing countries, China has a cost advantage in labor, energy, and raw materials. Although carbon fiber production is a technology and capital-intensive industry, China’s technical advancements and economies of scale have given its products a good cost-performance ratio in the international market. For example, the price of domestic T700-grade general-purpose carbon fiber is often more competitive than imported products, especially in price-sensitive fields like wind turbine blades and sports equipment.
3. Strong R&D Capabilities and Technological Breakthroughs
China has invested significant resources into carbon fiber technology research and development. Some enterprises and research institutions have made remarkable progress in the R&D of high-performance carbon fiber. For instance, Zhongfu Shenying Carbon Fiber Co., Ltd. (SYT) has successfully achieved stable mass production of T1100-grade ultra-high-strength carbon fiber, which indicates that China is now among the world’s leaders in the high-performance carbon fiber sector. These technological breakthroughs provide solid support for high-end applications like aerospace and defense.
4. Huge Domestic Market Demand
China has one of the world’s largest manufacturing systems, with huge demand for carbon fiber in industries such as wind turbine blades, automobiles, and sports equipment. According to CCF data, the total demand for carbon fiber in mainland China was approximately 79,000 tons in 2023, with wind turbine blades contributing over 40,000 tons of that demand, accounting for the vast majority. The vast domestic market provides a solid foundation for Chinese carbon fiber enterprises and a broad testing ground for the application of new technologies and product iterations, creating a virtuous cycle.
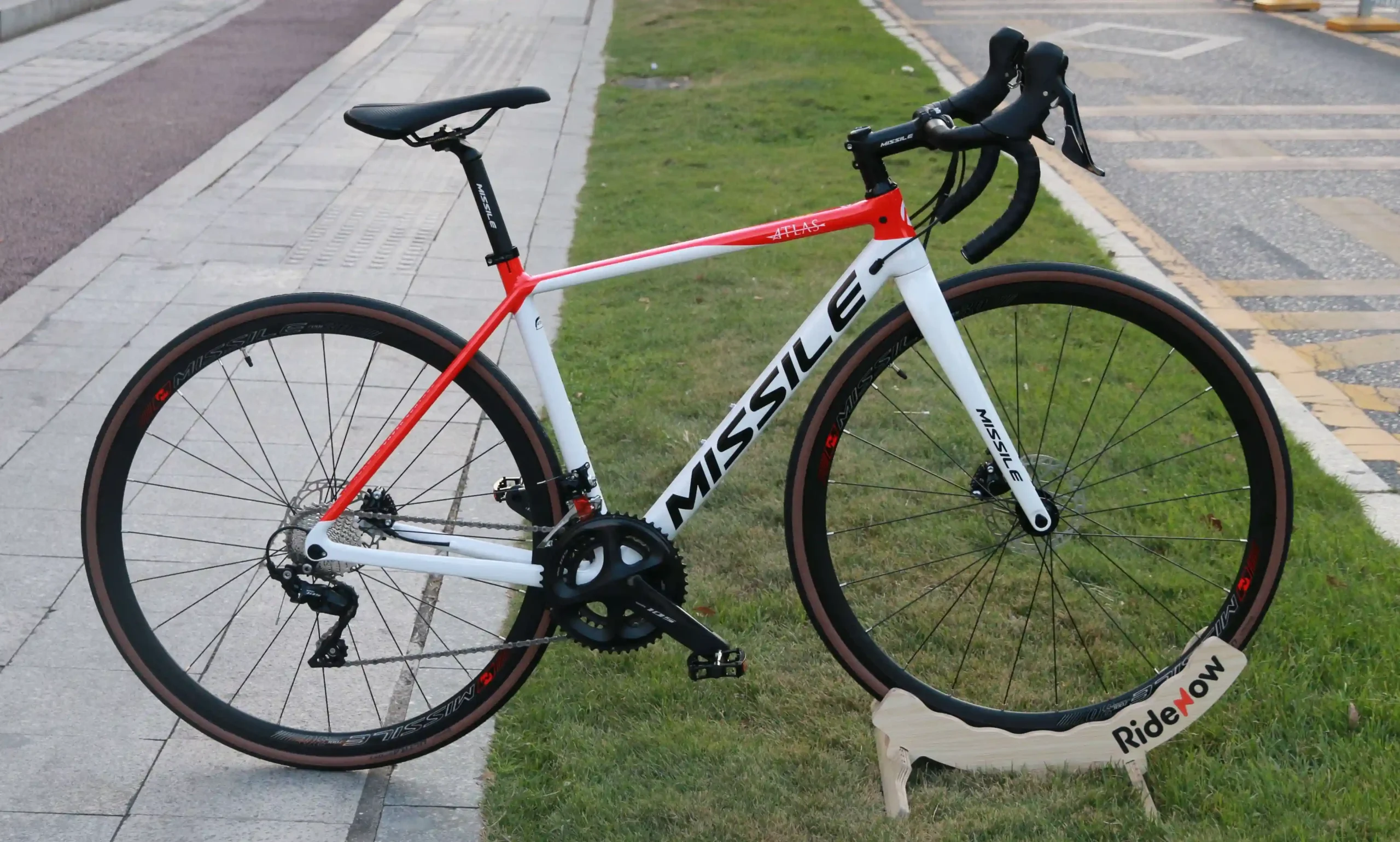

III. Main Specifications and Parameters
The performance of carbon fiber is typically measured by a series of key parameters that determine its suitability for various applications.
1. Strength
Tensile Strength: This is the maximum stress a carbon fiber can withstand before breaking under tension. It is the most important parameter for measuring the fiber’s tensile capacity, typically measured in Megapascals (MPa) or Gigapascals (GPa). For example, the tensile strength of T700-grade carbon fiber is usually around 4.9 GPa.
2. Modulu
Tensile Modulus: Also known as Young’s Modulus, it indicates the stiffness of the material during elastic deformation. A higher modulus means the material is more resistant to deformation. The unit is typically GPa. For example, the tensile modulus of high-modulus carbon fiber (such as M55J) can exceed 540 GPa, while T700-grade is around 230 GPa.
3. Density
Density: Refers to the mass per unit volume of the carbon fiber. One of the key advantages of carbon fiber is its high strength-to-weight ratio. The density of carbon fiber is generally between 1.7 and 2.0 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), which is significantly lower than steel (7.8 g/cm³) or aluminum (2.7 g/cm³).
4. Filament Count (Tow Size)
Filament Count: Refers to the number of individual filaments in a single tow of carbon fiber. Common sizes include:
-
-
- Small Tow: Typically 1K, 3K, 6K, or 12K, where K represents 1,000 filaments. Small tows are used for high-precision applications, such as aerospace and high-end sports equipment.
- Large Tow: Typically 24K, 48K, or higher, such as 320K and 480K. Large tows are more cost-effective and are commonly used in industrial applications, such as wind turbine blades and automotive parts.
-
5. Sizing
Sizing: A chemical coating applied to the surface of carbon fibers. This treatment improves the interfacial adhesion between the fiber and the matrix resin (e.g., epoxy resin), thereby enhancing the mechanical properties and processability of the composite material. Different sizing formulations are designed for specific resin systems.
IV. Industrial Clusters: Where to Find Carbon Fiber Manufacturers in China
The development of China’s carbon fiber industry shows distinct regional cluster characteristics, primarily concentrated in a few core areas. These clusters integrate R&D, production, and application resources, forming a complete industrial chain ecosystem.
1. Bohai Rim Region
-
- Core Cities: Weihai (Shandong), Yanbian (Jilin)
- Features: Represented by Weihai, Shandong, this is one of the earliest regions in China to develop carbon fiber. It has gathered leading companies like Ture Carbon and Guangwei Composites, forming a complete industrial chain from precursor fibers to carbon fiber and composite products. This region holds strong technological capabilities and market influence in aerospace, wind turbine blades, and sports equipment. Jilin, on the other hand, relies on scientific research institutions like the Chinese Academy of Sciences to play an important role in the R&D of high-performance carbon fiber.
2. Yangtze River Delta Region
-
- Core Cities: Lianyungang (Jiangsu), Hangzhou (Zhejiang), Shanghai
- Features: This area is centered around Zhongfu Shenying in Lianyungang, Jiangsu, which is one of the largest carbon fiber production bases in China. The Yangtze River Delta has a strong manufacturing foundation and R&D capabilities, attracting numerous downstream application companies. The cluster’s advantages lie in its strong capacity for technological innovation and its close integration with downstream industries like automotive manufacturing and wind energy, leading to a wide range of market applications.
3. Pearl River Delta Region
-
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Foshan (Guangdong)
- Features: The Pearl River Delta is known for its advanced manufacturing and innovative capabilities. The carbon fiber industrial cluster here focuses on downstream applications and technical services, especially in high-end consumer goods such as drones, 3C electronics, and sports equipment. This region leverages its strong market reach and supply chain advantages to quickly translate carbon fiber technology into commercial products, creating a unique industrial ecosystem.
V. Domestic Major Manufacturers (Leading Enterprises)
The rapid development of China’s carbon fiber industry is driven by a group of key companies with core technologies and large-scale production capabilities. These enterprises specialize in different fields, collectively forming the backbone of China’s carbon fiber sector.
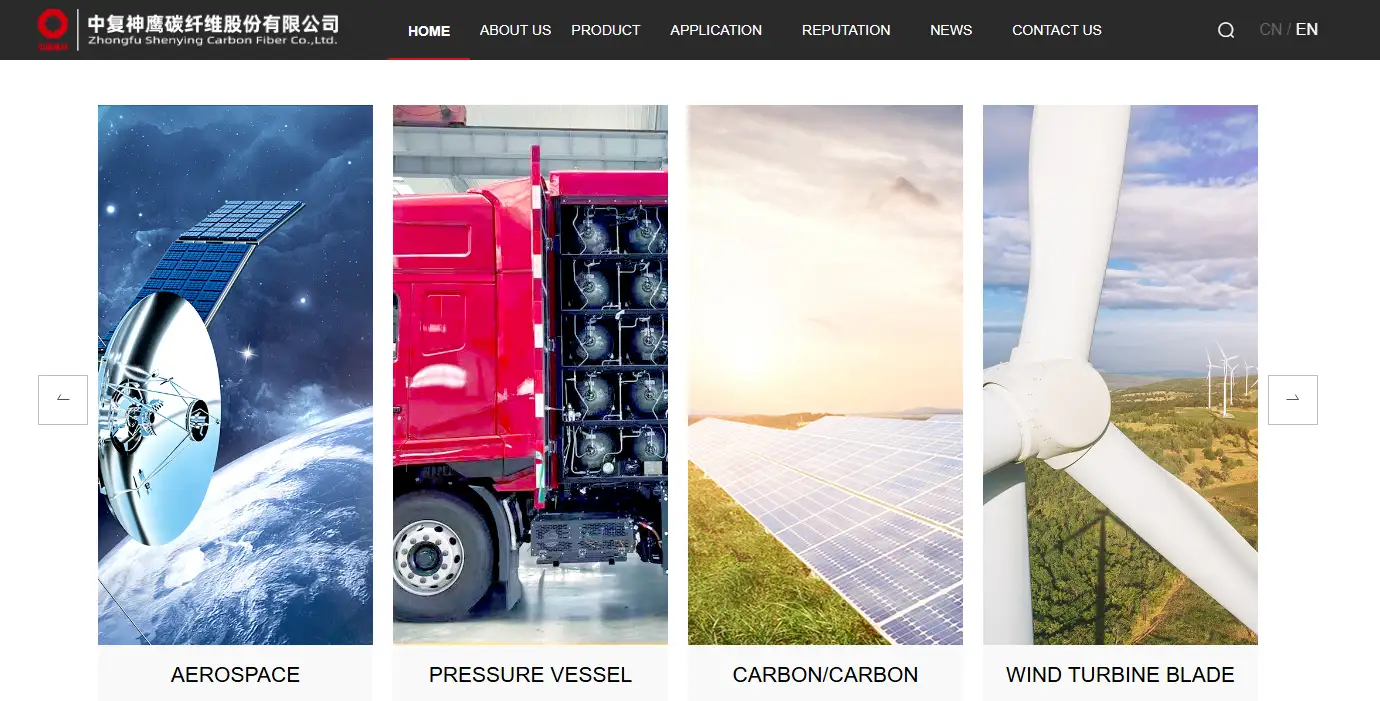
1. Zhongfu Shenying Carbon Fiber Co., Ltd. (SYT)
Zhongfu Shenying is a leading enterprise in China’s high-performance carbon fiber industry, focusing on the R&D and production of large-tow and high-performance carbon fibers. Its products are widely used in high-end applications such as aerospace, wind power, and pressure vessels. The company has successfully achieved stable mass production of T1100-grade ultra-high-strength carbon fiber, signaling that its technology has reached an internationally advanced level.
2. Jiangsu Hengshen Co., Ltd. (Hengshen)
Jiangsu Hengshen is one of the earliest companies in China to achieve industrialized carbon fiber production. Its business covers the entire industrial chain, from precursor fibers and carbon fibers to prepregs and composite products. Hengshen’s products are primarily used in aerospace, rail transit, automotive lightweighting, and industrial equipment, making it one of the few domestic companies that can provide full-chain solutions.

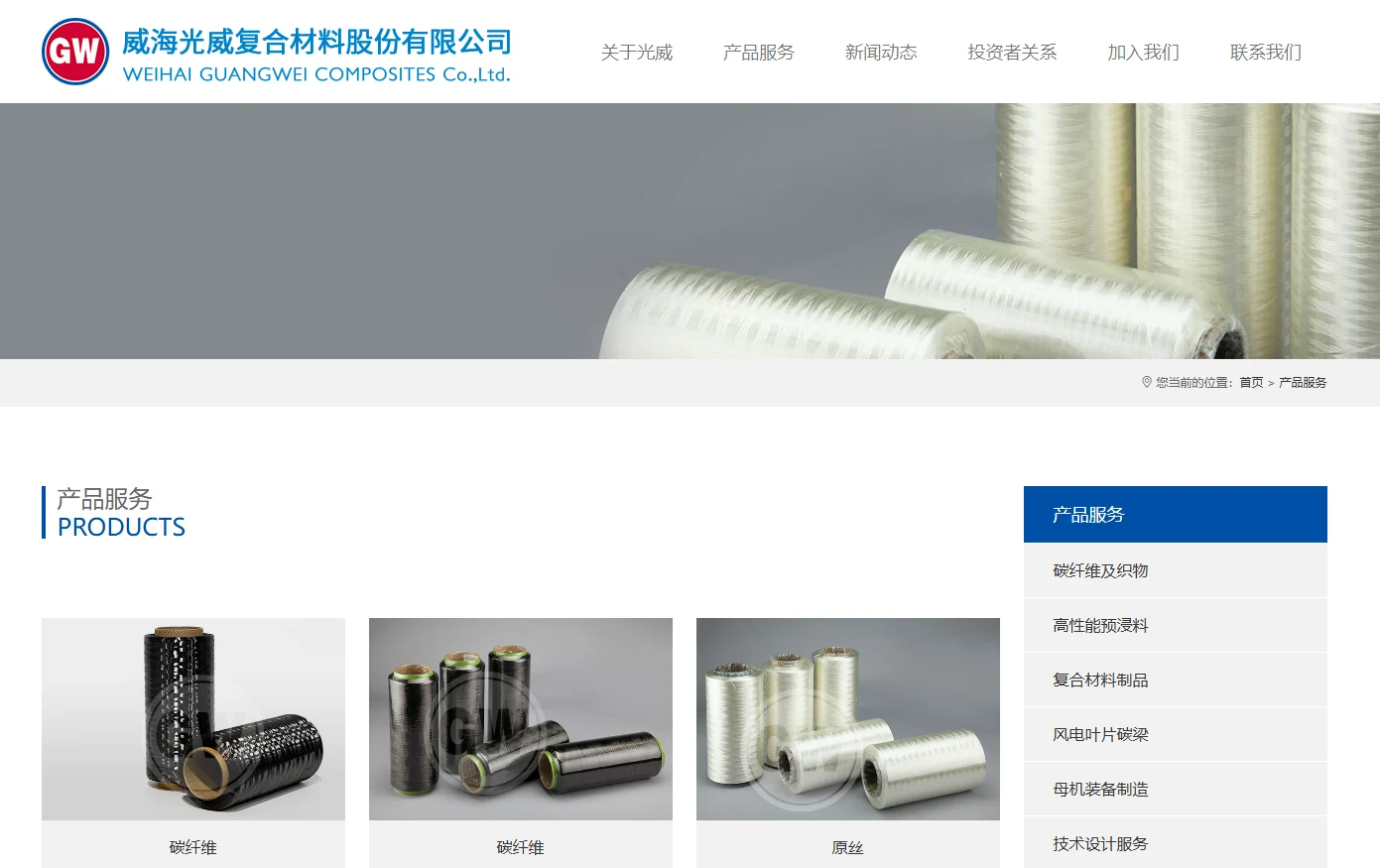
3. Weihai Guangwei Composites Co., Ltd. (Guangwei Composites)
Guangwei Composites is another significant player in China’s carbon fiber industry, holding a crucial position in the military and aerospace sectors. Known for its high-quality and stable products, the company primarily serves the defense and high-end sports equipment markets. Guangwei Composites has strong technical expertise and market advantages in the small-tow carbon fiber field.
4. Lanzhou Sigma New Material Co., Ltd. (Lanzhou Sigma)
Lanzhou Sigma specializes in the R&D and production of high-performance, high-strength carbon fibers. Its products are widely used in aerospace, wind turbine blades, sports equipment, and other fields. The company emphasizes technological innovation to continuously improve product performance and meet the customized needs of different clients.
VI. Relevant Certification Requirements
For Aerospace and High-End Markets
-
- AS9100/ISO 9001: This is the quality management system standard for the aerospace industry. A supplier with this certification demonstrates a strict commitment to quality control, capable of meeting the high reliability demands of the aerospace and defense sectors. While not a product certification, it is a key indicator of a supplier’s credentials.
- SAE AMS (Aerospace Material Specification): These are aerospace material specifications developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). Carbon fiber products must comply with specific AMS standards to ensure their performance and manufacturing processes meet the rigorous requirements of aerospace applications.
- Nadcap (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program): Nadcap is a worldwide program that audits the special processes (like composite manufacturing) of aerospace and defense suppliers. It certifies that the supplier’s manufacturing processes meet the highest industry standards.
For General Industrial and Consumer Goods Markets
-
- CE Marking (EU): When used as a component in certain end products (e.g., sports equipment, construction materials) entering the EU market, carbon fiber products may need to comply with health, safety, and environmental protection standards related to the CE Mark.
- ISO 14001: This is an environmental management system standard. For environmentally conscious buyers, especially for applications like wind turbine blades that require sustainability, a supplier with ISO 14001 certification can demonstrate its commitment to environmental management.
- ISO 45001: This is an occupational health and safety management system standard. It indicates that the manufacturer is committed to providing a safe working environment for its employees, which is an important consideration for some socially responsible importers.
Crucial Tip
Always request and verify the official certification documents and test reports for the specific carbon fiber models you plan to import. Do not rely solely on a supplier’s verbal assurances to ensure your products can smoothly enter the international market and comply with regulations.
VII. Precautions for Purchasing: Making an Informed Decision
Once you have identified potential Chinese carbon fiber suppliers and their products, follow these steps to ensure a successful purchase.
1. Start with Small Batches or Samples
Before placing a large order, it is highly recommended to procure a small batch or a sample. This allows you to perform a hands-on quality assessment of the carbon fiber’s quality, specifications, and consistency. Test its tensile strength, modulus, density, and sizing to ensure it meets your technical requirements.
2. Assess Supplier Production Capacity
A supplier’s production capacity is a crucial indicator of their ability to meet your demands, especially for large orders. Inquire about their production metrics, manufacturing processes, and delivery timelines. A well-established manufacturer with high output and a stable supply chain is more likely to handle your orders efficiently.
3. Clearly Define Your Application Needs
Be specific about how you will use the carbon fiber. Is it for high-end structural components in aerospace, or for general-purpose industrial applications like wind turbine blades? Different applications have specific requirements for fiber strength, modulus, tow size, and sizing, which will dictate the product model you choose.
4. Consider Technical Support and Customization
A reliable supplier should be able to provide technical support, including application advice and customization services. Inquire if their technical team can assist you with integration and processing challenges, and whether they offer customized products for specific needs.
5. Calculate Total Cost
Remember to account for all costs beyond the unit price. This includes shipping fees, insurance, import duties, customs clearance costs, local taxes, and potential costs for third-party quality inspections and verification.
6. Perform Due Diligence
Utilize third-party audit services to verify a supplier’s credentials and factory conditions. Request to see their quality management system certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) and relevant product test reports. If possible, ask for references from other international buyers.
VIII. Choose IMEXsourcing Partner for Carbon Fiber in China
When it comes to procuring high-quality carbon fiber from China, partnering with an experienced and reliable IMEXsourcing agent is paramount. A good agent offers a comprehensive suite of services designed to streamline your acquisition process and secure exceptional value. Here are compelling reasons to select an IMEXsourcing partner for your next carbon fiber purchase:
Extensive Procurement Expertise
A professional IMEXsourcing agent boasts a profound and long-standing history in the IMEXsourcing industry, enabling them to proficiently locate and secure a wide array of carbon fiber products from highly regarded Chinese suppliers. Their deep market knowledge ensures that they connect you with manufacturers known for their reliability and superior products.
Bespoke Design Solutions
A great agent understands that unique requirements often demand tailored solutions. They empower you to commission carbon fiber products precisely engineered to your specifications, ensuring the final product perfectly aligns with your operational needs.
Thorough Supplier Verification
The commitment to quality begins with rigorous due diligence. A professional agent conducts comprehensive factory verifications for all potential manufacturers. This meticulous audit confirms their production capabilities, assesses their quality control protocols, and ensures their full compliance with relevant industry standards and legal requirements.
Expert Price Negotiation
A professional agent excels in negotiation. This invaluable expertise allows them to secure the most favorable pricing and terms with top-tier carbon fiber manufacturers, optimizing your investment.
Stringent Quality Assurance
A professional agent implements a robust quality management framework that spans the entire procurement cycle. This includes careful selection of suppliers, diligent oversight through production inspections, and thorough product testing prior to shipment, guaranteeing the integrity and performance of your carbon fiber.
IX. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Chinese carbon fiber market offers a wealth of opportunities for global buyers. By carefully researching product types, understanding technical specifications, and following a structured procurement process, importers can find high-quality, cost-effective carbon fiber materials to meet a variety of application needs.
Moreover, engaging with reputable suppliers and conducting thorough due diligence ensures that the procurement process is not only efficient but also minimizes risks associated with international trade. IMEXsourcing is highly professional in the carbon fiber sector, with multiple successful experiences in carbon fiber export and quality inspection, and can provide you with reliable assistance. This strategic approach not only enhances the value proposition but also fosters long-term business relationships, ultimately contributing to sustained profitability and market competitiveness.